Getting started with Enterprise App Management
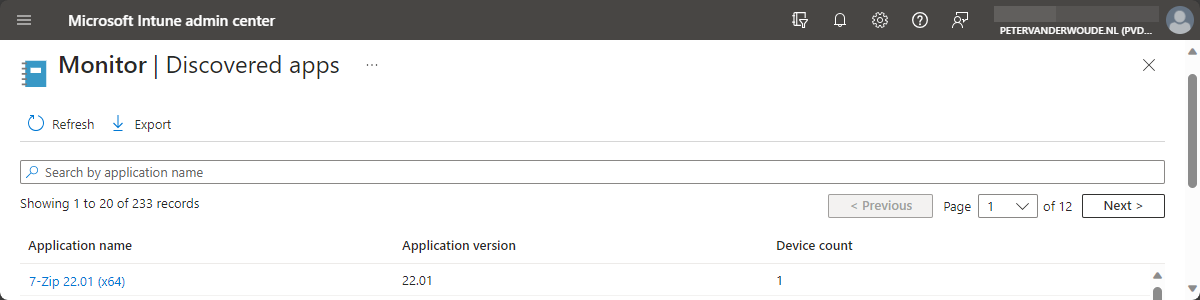
This week is sort of a follow-up on the earlier post about new Microsoft Intune Suite add-on capabilities. That time it was around the early capabilities, like Endpoint Privilege Management, the first glimpses of Advanced Analytics, and Microsoft Tunnel for MAM. This time it’s about Enterprise App Management. Enterprise App Management provides organizations with an applications catalog that contains apps that are prepared by Microsoft. Those apps are all Win32 apps that are wrapped and hosted by Microsoft. That can further simplify management and makes sure that the lifecycle of apps is getting better under control. That means more structural updates of apps, which makes sure that the environment gets more secure. This post will start with a further introduction about Enterprise App Management, followed …